How to Prune Apple Trees
Basic pruning principles, like those found in our free nine part fruit tree pruning course, apply to all fruit trees, but specific trees have specific needs that should be addressed in the pruning process. Over the next several weeks we will do a deep dive into all of the most popular fruit tree varieties and how their pruning differs from one another.
For regular updates on the care and pruning of fruit trees, please subscribe here.
Unlike stone fruit, apples only produce blossoms on the terminal bud. Lateral buds only grow leaves. This is an important detail for understanding how to prune apple trees.
After apple trees are pruned, they will grow lots of water sprouts. Water sprouts are fast growing branches with lots of lateral buds which are designed to leaf out and help the tree collect solar energy that it then uses to grow around pruning cuts to seal them off from pathogens. Water sprouts that grow around larger pruning cuts can help prevent heartwood rot.
Though water sprouts serve an important purpose, they grow in excess and most need to be removed. Water sprouts that are stimulated by structural pruning can be used to help direct and grow a young apple tree. When maintenance pruning apple trees, the majority of the pruning cuts will be made by thinning out water sprouts year after year. These fast growing branches will shade out the more productive branches found on older wood. When corrective pruning, water sprouts are used to replace overgrown, unproductive, diseased, or damaged branches. To avoid excess water sprouts, you can prune large apple trees in the fall. The dormant period and cool temperatures will, in a way, cauterize the pruning cuts so that they don't proliferate in the spring. This does cause those same pruning cuts to heal slowly, making them more susceptible to disease. Water sprouts can also be removed when they are still small and herbaceous in the summer, before they harden off and become woody.
The fruiting branches on apple trees are called spurs. These slow growing branches are extremely valuable because they are found on older, sturdier branches near the interior of the tree. Apples are heavy and too many apples on one branches can cause branches to break, that is why spurs on mature branches should be protected from damage.
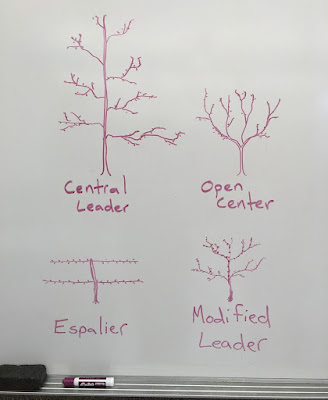
Apple trees can mature and ripen fruit with less sunlight than peaches and nectarines. By pruning apple trees with a central leader or a modified leader, you can increase the surface area of the tree, thus increase production.
Not all apple tree's are created equal. Red delicious apple trees, for example, grow lots of spurs, making them extremely productive trees. Honeycrisp apple trees, on the other hand, do not readily grow spurs and are less productive. Some Apple trees will grow spurs on two year old branches, others will take four or five years to develop.
Apples are susceptible to a diverse number of diseases and it is important to correctly identify diseases in apple trees prior to pruning. Fire blight, for example is a extremely contagious disease and can be spread during the pruning process. Follow this link to learn more about managing fire blight in apples and pears.
Thanks for Reading! If you would like to learn more about the care and pruning of fruit trees, please browse our 100+ fruit tree articles here, join our Backyard Fruit Growers Facebook Group, and take our free Fruit Tree Pruning Course. Also, please subscribe to our Fruit Pruning YouTube Channel.










well done! ty
ReplyDeleteGlad to help
Delete